● JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)
-자바를 이용한 데이터베이스 접속과 SQL 문장의 실행, 그리고 실행 결과로 얻어진 데이터의 핸들링을 제공하는 방법과 절차에 관한 규약
-자바 프로그램 내에서 SQL문을 실행하기 위한 자바 API
-SQL과 프로그래밍 언어의 통합 접근 중 한 형태
-JAVA는 표준 인터페이스인 JDBC API를 제공
-데이터베이스 벤더, 또는 기타 써드파티에서는 JDBC 인터페이스를 구현한 드라이버(driver)를 제공한다.
● JDBC 환경 구성
-JDK 설치
-JDBC 드라이버 설치
→ Maven에 다음과 같은 의존성을 추가한다. MySQL 사이트에서 다운로드한다.
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupid>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.45</version>
</dependency>
* 참고 사이트
Java Platform SE 8
docs.oracle.com
Lesson: JDBC Basics (The Java™ Tutorials > JDBC(TM) Database Access)
The Java Tutorials have been written for JDK 8. Examples and practices described in this page don't take advantage of improvements introduced in later releases and might use technology no longer available. See JDK Release Notes for information about new fe
docs.oracle.com
● JDBC를 이용한 프로그래밍 방법
1. import jaja.sql.*;
2. 드라이버를 로드한다
3. Connection 객체를 생성한다.
4. Statement 객체를 생성 및 질의 수행
5. SQL문에 결과물이 있다면 ResultSet 객체를 생성한다.
6. 모든 객체를 닫는다.
● JDBC 클래스의 생성 관계
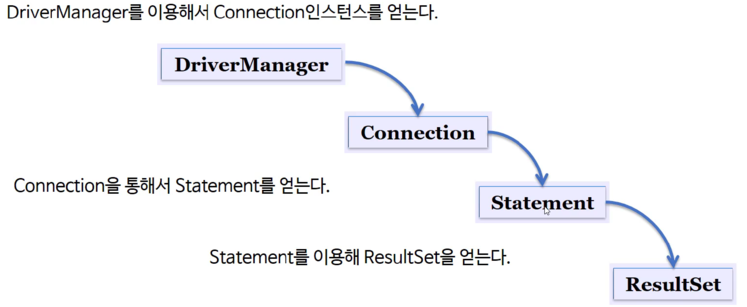
● JDBC 클래스의 생성 단계
1. IMPORT
import java.sql.*;
2. 드라이버 로드
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driber");
3. Connection 얻기
String dburl = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/dbName";
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(dburl, ID, PWD);
소스코드 예제
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception{
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@117.16.46.111:1521:xe";
String user = "smu";
String password = "smu";
Connection conn = null;
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
conn = DriveManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
return conn;
}
4. Statement 생성
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
5. 질의 수행
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("select no from user");
참고
stmt.execute("query"); // any SQL
stmt.executeQuery("query"); // SELECT
stmt.executeUpdate("query"); // INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
6. ResultSet으로 결과 받기
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("select no from user");
while (rs.next())
System.out.println(rs.getInt("no"));
7. Close
rs.close();
stmt.close();
con.close();
소스코드 예제
public List<GuestBookVO> getGuestBookList(){
List<GuestBookVO> list = new ArrayList<>();
GuestBookVO vo = null;
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try{
conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from guestbook";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
vo = new GuestBookVO();
vo.setNo(rs.getInt(1));
vo.setId(rs.getString(2));
vo.setTitle(rs.getString(3));
vo.setContent(rs.getString(4));
vo.setRegDate(rs.getString(5));
list.add(vo);
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
DBUtil.close(conn, ps, rs);
}
return list;
}
소스코드 예제
public int addGuestBook(GuestBookVO vo){
int result = 0;
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try{
conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into guestbook values("
+ "guestbook_seq.nextval,?,?,?,sysdate)";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1,vo.getId());
ps.setString(2,vo.getTitle());
ps.setString(3,vo.getContent());
result = ps.executeUpdate();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
DBUtil.close(conn, ps);
}
return result;
}
소스코드 예제
public static void close(Connection conn, PreparedStatement ps){
if(ps != null){
try{
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
if (conn != null){
try{
conn.close();
} catch(SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();}
}
}
다음 시간에는 실제로 JDBC를 좀 더 사용해보겠다.
'CS > Database' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [MYSQL] 사용법 정리 (0) | 2020.05.19 |
|---|---|
| [Edwith] 9. Maven (0) | 2020.04.20 |
| [Edwith] 8. DDL 알아보기 (0) | 2020.04.16 |
| [Edwith] 7. DML - DELETE 알아보기 (0) | 2020.04.16 |
| [Edwith] 6. DML - UPDATE 알아보기 (0) | 2020.04.16 |

